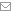
Gypsum
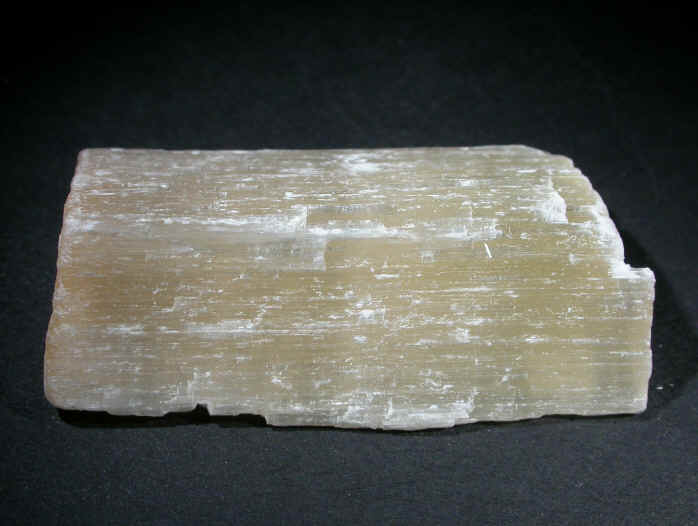
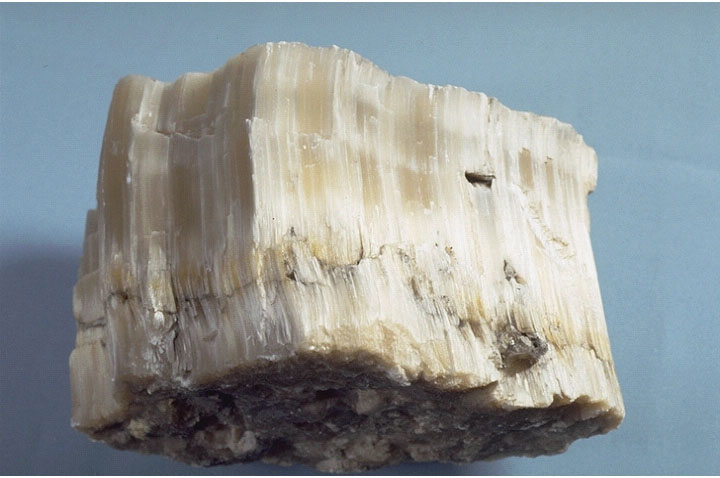
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dehydrate, with the chemical formula CaSO4·2H2O. It can be used as a fertilizer, is the main constituent in many forms of plaster and in blackboard chalk, and is widely mined.
Gypsum is an evaporite mineral most commonly found in layered sedimentary deposits in association with halite, anhydrite, sulfur, calcite and dolomite. Gypsum is the most common sulfate mineral.
Gypsum uses include: manufacture of wallboard, cement, plaster of Paris, soil conditioning, a hardening retarder in Portland cement. Varieties of gypsum known as "satin spar" and "alabaster" are used for a variety of ornamental purposes, however their low hardness limits their durability.